Dried Apricots
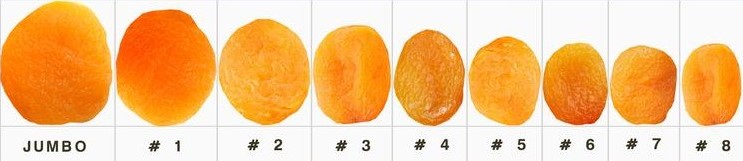
Berry Sizes
| Size No. | Diameter | Count per kg. |
| 1 | 36 mm or larger | up to 100 |
| 2 | 32 – 36 mm | 101 – 102 |
| 3 | 29 – 36 mm | 121 – 140 |
| 4 | 26 – 32 mm | 141 – 160 |
| 5 | 24 – 29 mm | 161 – 180 |
| 6 | 24 – 26 mm | 181 – 200 |
| 7 | 21 – 26 mm | 201 – 220 |
| 8 | 20 mm or less | 220 or more |
Harvest, Drying and Packing of Dried Apricot
Harvest:Harvest time is determined with respect to the type of apricot, the altitude at which it is grown, the ripening, the getting yellow of its colour, its softening and getting sweet and juicy. The most suitable apricot harvest is made by hand, so the fruits are not damaged during harvest and they are harvested when sufficiently ripe. The other harvest types are that are done by shaking and flapping.
Drying: Apricot is dried for using two different methods, called “Gün kurusu” (natural dry) and “Kükürtleme” (sulfured dry). Sulfuring is useful to shorten the time of the drying process, to preserve the natural colour, to prevent the product from getting infested with bugs and to increase the preservation period. Sulfuring, and the rest accomplish more than 80 % of the total drying efforts by drying in the sun. Spreading the apricot directly on earth, concrete, or cloths does 10 % of the drying processes.
In natural drying, the quality decreases because of the dirt and bruises that the apricots receive. In apricots that are day dried, bugs form a short time after the drying process, but nevertheless, these apricots are very tasteful.
Selecting and Packing: Drying process is made by growers and farmers and then these raw apricots are sold in the market to intermediaries. These merchants market the apricots to processor and packer companies. Packers companies first wash and fumigate these apricots, then calibrate to 8 different sizes, after these processes, apricots are waited in plastic baskets for 24 hours to absorb the excess water in it. After humidity and SO2 tests, if the product is conformed to official quality standards, handpicked by workers one by one. All the wounded, damaged, dotted and mouldy berries are selected.
The final outcome is put into generally 5 or 12.5 kg bulk cartons, inside pp nylon or oil paper. In many of processing and packing houses, retail packs like 200, 250, 400, and 500 gr is workable upon requests of buyers. These are white foam trays or clear cello bags.
Dried apricot is generally consumed as
1. Snacking
2. In Bakery (3-5 mm or 7-9 mm dice form is workable)
3. Confectionery
4. Compote
Nourishing Value and Benefits for Human Health
Through the organic and inorganic substances it contains, apricot affects human health positively. Apricot contains a large amount of sugar, starch, protein, pectin, pectose, cellulose, vitamins and acids. Apricot is very rich of the mineral potassium and the vitamin ß carotene. Vitamin A is necessary for the health of the epithelium tissue surrounding the body and the organs, and for the health of the eye, for the health of bones and teeth, and for the functions of the endocrine glands. A diet of 200-250 grams of apricot contains sufficient oil and 1/3 of the necessary amount of vitamin A for one day. The property of apricot about being poor in sodium and rich in potassium may help the arrangement of some special diets. Sodium and potassium is necessary for the osmotic pressure and the acid-base equilibrium of the body fluids. Sodium accumulation in the body leads to edemas.
Insufficiency of potassium leads to insufficiency of glycogen. Apricot can conveniently be used in diets where sodium is restricted, for example in diets for congestive cardiac insufficiency, in renal illnesses, in hematite cirrhosis where, acid accumulates, and excess in the diets for persons having long times of carticosteroide therapy.
Benefits for Health
1. Helps brain functions, decreases stress
2. Heals the damaged part of liver
3. Is useful for bones
4. Is useful against anemia
5. Prevents ulcer formation and helps the healing of ulcers
6. Decreases the formation of kidney stones
7. Increases sexual power
8. Has a protecting effect against cancer
9. Helps teeth to be stronger and healthier
10. Strengthens the cardiac muscles and helps them to function smoothly, thus is effective in the heart’s ability to recover during the reanimation efforts in a clinic death, if the person has eaten apricot a sufficient time before the event.
11. It’s very important in nourishment because while it is rich in potassium and carotene, it is poor in sodium.
| Nutrition Information (100 gr.) | |
| Energy | 267 kcal (1117 kJ) |
| Protein | 3,1 g |
| Carbohydrate | 62,8 g |
| Fat | 0,48 g |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium | 67 mg |
| Iron | 5,5 mg |
| Magnesium | 62 mg |
| Phosphorus | 108 mg |
| Sodium | 26 mg |
| Potassium | 979 |
| Vitamins | |
| A (IU / ug) | 10,900 (IU) |
| B1 | 0,01 mg |
| B2 | 0,16 mg |
| B3 | 3,3 mg |
| C | 12 mg |










